Accessible Materials for All Students

Accessible educational materials (AEM) can play an important role in ensuring students with disabilities are able to continue their education without a significant disruption during eLearning Days. In addition to the opportunities they provide for learners with disabilities to continue their education, accessible educational materials have benefits for all learners. This page includes resources to support students with IEPs and resources to create and curate accessible educational materials.
AEM Center Office Hours
AEM hosts weekly webinars with office hours following the webinars each week:
Tuesdays, 10 – 11:30 AM ET and Thursdays, 4 – 5:30 PM ET
Additional AEM Resources for Access and Distance Education
Supporting Students with IEPs During eLearning Days
 Suggestions from the National AEM Center
Suggestions from the National AEM Center
Continuing special education services during eLearning Days is essential to the participation and progress of students with IEPs. Under the circumstances of school closures due to the current COVID-19 outbreak, the U.S. Department of Education issued a Q&A document on March 12, 2020. On page 2, the Department makes clear that – when educational opportunities continue to be provided during a school closure – states, districts, and schools “must ensure that, to the greatest extent possible, each student with a disability can be provided the special education and related services identified in the student’s IEP developed under IDEA, or a plan developed under Section 504.”
How can districts support students with IEPs or 504 plans during eLearning Days? Here are some suggestions:
Administrators
- Provide expectations, guidelines, and processes for supporting the independence, participation, and progress of students with disabilities during eLearning Days. These should include coordination among general education, special education, assistive technology (AT), and educational technology personnel.
- Schedule opportunities for special education teachers and general education teachers to collaborate on the development of curriculum and instruction for eLearning Days.
Special Education Teachers
- Coordinate with general education teachers to ensure that your shared students’ accommodations and modifications continue to be provided during eLearning Days. Follow guidance provided by your district so that electronic communications protect student privacy.
- Maintain as much consistency as possible on the delivery of specialized instruction, including the same materials and tools used at school.
- Set a schedule of personal communications with the students on your caseload (and/or their families as appropriate) to check on their progress. Be as specific as possible, such as asking if their AT is working as expected and if they’re clear about their accommodations or modifications on assignments. If problems are evident, coordinate a solution with the appropriate personnel (i.e., general education, educational technology, assistive technology).
General Education Teachers
- For general education teachers:
- Understand your students’ IEPs and 504 plans, and implement the accommodations, modifications, and goals related to your curriculum and instruction.
- Coordinate with your students’ special education teacher(s) as you plan your eLearning curriculum and instruction to ensure that students with IEPs and 504 plans have access to the materials and technologies, and that their goals can be met.
- Use formative assessment so that all students’ progress can be monitored during eLearning Days. If it’s evident that a student with an IEP or 504 plan is not making progress, communicate with the student (and/or their family as appropriate) and work with their special education teacher to problem solve as soon as possible.
Tech Directors and Tech Coaches
- For educational technology directors and technology integrators:
- Know the assistive technologies being used by students in the district. Just like classroom technology, these should be tested for interoperability with the district technology being used for general curriculum during eLearning Days.
- Be available to students who use AT and their families during eLearning Days.
Educating All Learners
The Educating All Learners Alliance (EALA) is an uncommon coalition of organizations committed to resource sharing and community-building that supports the efforts of the education community to meet the needs of students with disabilities during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Creating Accessible Educational Materials
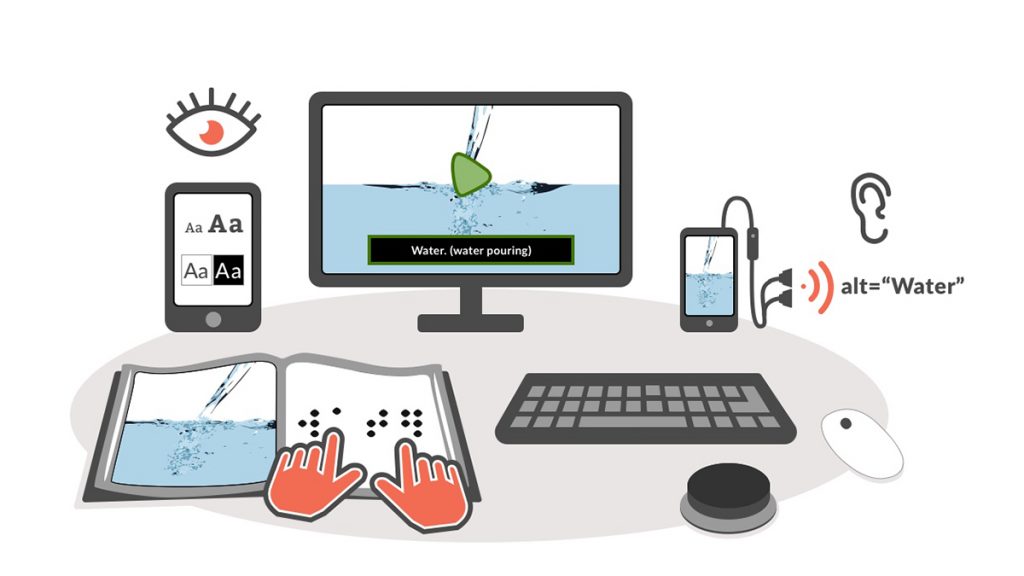
The AEM Center and CAST provide a number of resources that can help educators create and share accessible educational materials for students impacted by school closures. Whether content is uploaded to a learning management system (LMS) or shared with families through email, it is important to ensure information is made accessible and meets the needs of a variety of learners while they are unable to attend school.
Developing Accessible Educational Materials
Quick Handouts: These handouts use the mnemonic SLIDE (for Styles, Links, Images, Design and Empathy) to make the best practices easier to remember.
- Getting Started with Document Accessibility
- Getting Started with Presentation Accessibility
- Best Practices for Accessible Social Media
- Top Ten Tips for Creating Quality Videos
Websites & Tools:
- Is It Accessible? Questions to Ask: This document is meant to accompany the Designing for Accessibility with POUR resources. It consists of a series of questions educators can use to evaluate the accessibility of materials based on the four POUR principles.
- Teaching with Accessible Video: Video will likely play a role in any kind of online learning initiative, as both a way to deliver content and to maintain communication with families and the community. This resource was designed as an extension of Module 3 of the AEM Center online modules and provides more detailed information about the benefits of accessible video, where to locate videos with high-quality captions, and how to get started with captioning.
- Accessible Math: This page provides an overview of classroom tools for making math content more accessible with supports such as text to speech for reading math expressions aloud and handwriting recognition or speech to text to provide options for how learners respond and work through problem sets.
- Personalizing the Reading Experience: Families may not be aware of the many accessibility features that are built into the devices many of them may already have at home, including their tablets and smartphones. This resource focuses on supports for creating a personalized reading experience for every learner through customized display settings and free or low cost text to speech solutions.
- Website Designing for Accessibility with POUR: The four core principles of an accessible experience as defined by the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are explained in plain language and supported by links to videos and other online resources that illustrate how to put each principle into practice.
- Alternate Versions of Print Materials: AEM Guide: The Individuals with Disabilities Act (IDEA) contains important requirements regarding the timely provision of printed textbooks and related printed core materials in accessible formats to students with visual, physical, and other disabilities that prevent reading and using information in traditional printed materials. This resource includes information about the three major accessible media producers (AMPs) that provide alternative versions of print materials to eligible students: Bookshare, Learning Ally and American Printing House for the Blind.
- Mathshare is the first-of-its-kind inclusive digital math editor that gives all students (with and without disabilities) the unprecedented ability to freely interact with math problems online and to easily demonstrate their math skills in a digital environment. As more classrooms utilize online learning environments, millions of students increasingly face challenges in solving math problems online and showing their work. Mathshare enables all students to learn how to solve math equations by themselves, make errors, start again independently, and show their work to their educator in a digital, accessible, and user-friendly environment.
Online Course for Educators
- Making Everyday Curriculum Materials Accessible for All Learners: A year-long learning experience on accessible educational materials that is now archived on the AEM Center website. Each module includes a recorded webinar that provides background knowledge on the topic, along with links to relevant AEM Center resources and activities for reflection and application. We recommend starting with the following two modules:
Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
UDL is a framework that guides the design of learning experiences to proactively meet the needs of all learners. When you use UDL, you assume that barriers to learning are in the design of the environment, not in the student. UDL is based on brain science and evidence-based educational practices. It also leverages the power of digital technology.
- UDL Guidelines: A set of principles for designing curriculum that provides all individuals with equal opportunities to learn, through the proactive application of Universal Design for Learning.
- UDL Tips: Provides practical tips for addressing specific aspects of UDL in the design of learning environments (learning goals, assessment and more).
- UDL Exchange: Allos educators to create, mix, and share instructional resources, including lesson plans, based on UDL and aligned to standards.
- UDL Studio: Allows educators to make universally designed educational materials with levels of learning support.
- UDL Book Builder: Enables preK-12 educators to develop their own digital books to support reading instruction literacy learning.
More detailed information about the best practices introduced in the handouts is available throughout the AEM Center website.



